The knee joint is arthrosis or osteoarthrosis is a disease that occurs in the background of dystrophic changes with the later increase in connective tissue.There are many factors that affect the development of the disease, but each eventually leads to a violation of cartilage metabolism.In medical literature, the arthrosis of the knee joint is called gonarthrosis.
According to statistics, gonarthrosis occupies a leading position in the frequency of occurrence between other joint parts.The disease causes severe discomfort that can turn into pain during walking and relaxation.
Knowledge of early symptoms promotes suspicion of pathology and healing in the initial stages.
Reasons
According to medical classification, the knee joint is primary and secondary gonarthrosis or arthrosis.
The arthrosis of the knee joint can occur in the background of various diseases or act as a complication.When the exact cause cannot be determined by the unclear history or clinical picture, gonarthrosis is called primary, but if the cause is known, such arthrosis is called secondary.
Arthrosis develops at age for almost all people, and this period begins after an average of 45-50 years.
The pathogenesis and pathogenesis of primary and secondary arthrosis are the same and does not depend on the cause of the occurrence.
The most common causes of the knee joint arthrosis and osteoarthrosis are as follows:
- Traumatic damage to the knee;
- joint deformation inward and outside;
- Abbreviation for a lower limb;
- Abnormal hypermobility of the joint;
- Chondroblast dysplasia;
- Cartilage calcinosis;
- Osteomyelitis of the femur and tibia;
- Any other etiology rheumatoid arthritis or arthritis;
- glucose metabolism;
- Metabolic diseases and hormonal diseases.
Injuries.Once the knee injury is obtained in the joint cavity, the alternation may result in a high emphasis on inflammation.After the disappearance of Pro -inflammatory agents, the process of repair or arthrosis is activated.
Most often, the disease occurs in the background of the fracture, interrupting the leagues, damage to the cartilage surface of the bag and joint.
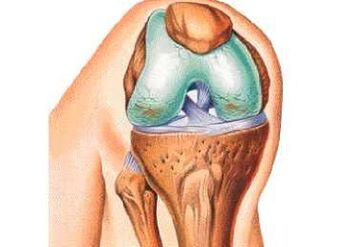
Congenital deformations.Valgus or variation deformation can become very often and without proper correction with sclerotic changes in the knee.This is because one knee falls more than the load than it should be.
Abbreviation for any of the lower limbs.In the pathogenesis of the disease, in addition to deformations, the knee is not properly distributed in the knee.
The knee hypermorai.In this condition, the abrasion of the cartilage tissue of the knee joint may occur with later degeneration and degeneration into arthrosis.Hypermore often leads to spontaneous dislocations and joint capsule jerks.
Hand -haired dysplasia.Due to the inadequate development of the motor surface of the engine surface, the abnormal increase in connective tissue occurs.
The joint calcinosis.Pathogenesis is based on the deposition of salts into the joint cavity and the formation of a specific precipitation, which causes calcification for later osteoarthritis.
Osteomyelitis.An inflammatory bacterial disease in which the destruction of bones and joints.First, ankylosis and only then develop sclerosis.
Any etiology arthritis.The most dangerous is rheumatoid arthritis, accompanied by autoimmune lesions of the heart and joints.
Diabetes, as well as metabolic disorders, leads to a violation of the flow of nutrients into the joint and the cartilage.
Obesity.With the heavy weight of the body, heavy load is on the knees, walking and standing.As a result of constant pressure, blood flow to the knee joints is reduced and dystrophy develops atrophy.
Symptoms
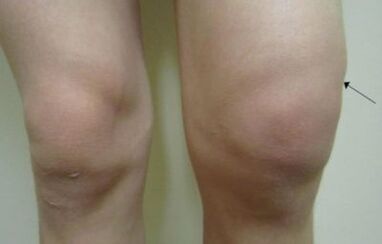
Symptoms associated with arthrosis of the knee joint depend on the stage of the pathological process.On this basis, based on the analysis of the pace of symptoms and growth, you can assess the degree of cartilage tissue changes.
Symptoms of knee arthrosis:
- the presence of abnormal sounds during movement;
- pain after load or tranquility;
- reducing functions;
- edema and joint growth;
- pathological dislocations, fractures and subluxation;
- Temporary jam that can occur when the joint is bending and extending.
Clicking and cracking are not immediately noticed, and if you notice it, they will not pay enough attention.Pathological sounds are confronted with the idea that in the cartilage, the abnormal process involves salt or the formation of osteophytes occurs.
Pain is due to the formation of calcinates or osteophytes.Initially, the pain syndrome does not express, later it only appears in the morning and disappears after lunch, and with the progression of the disease, the pain can occur at rest.
The decrease in arthritis is reflected in the stiffness of movements and the reduction of its amplitude.Depending on the stage, the restriction of movements can take some time and pass on.
Edema is a consequence of synovial fluid inflammation and hypersecretion.There are also opportunities where the skin is inflamed above the joints.Such symptoms can be scarlett or rheumatism.
Dislocations and subluxation occur to the process of the knee bones and ligaments.
Library is a condition in which the axes of the axes are completely limited.Such a symptom indicates neglecting the process and the need for complex treatment.
Articular
You can classify osteoarthritis as follows:
- radiological symptoms;
- clinical manifestations;
- Laboratory data.
The most common and comfortable classification is radiological, simple and understandable, even for people without medical education.
According to X -Srays, four degrees of arthrosis in the knee joint can be distinguished:
- Reduction of joint gap and there are no osteophytes;
- The Interspoint gap is not indicated, but there are signs of small calcinates or osteophytes;
- The Interspoint gap has a narrowing expression, there is osteophytes, and the joint deformation begins;
- The lack of joint gap, bone deformation, anchilose and dystrophy.
As regards the clinical picture, the following sections distinguish:
- Mild symptoms are insignificant, occur in the morning and pass 30-60 minutes after waking up;
- The average degree of symptoms, the feeling of discomfort before lunch, the swelling is insignificant, without treatment without treatment;
- Severe degree - which is characterized by constant pain, the inconvenience of tranquility, the morning stiffness, while dinner, ankilose, burgis and knee joints occur.
Laboratory tests are taken into account and soy and leukocytes are evaluated.The presence of the rheumatoid factor should also be checked.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of the arthrosis of the knee joint is not complicated, but requires certain skills from the doctor.
Two types of diagnostic measures are distinguished:
- laboratory diagnostics;
- Instrumental diagnostics.
For the right diagnosis, each method must be taken into account and the image must be analyzed as a whole.
Laboratory
If you suspect arthrosis, the participating doctor will prescribe the following tests:
- General blood and urine testing;
- Biochemical blood test;
- determination of antibodies against rheumatoid factor;
- Determination of antibodies against their own cells.
Laboratory data does not provide information on the stage of the disease.
Instrumental
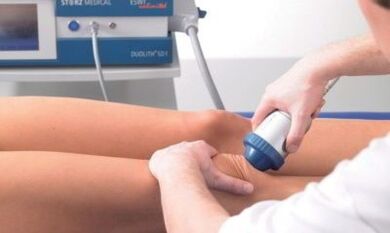
The instrumental diagnosis of arthrosis contains the following methods:
- Radiography in two standard predictions;
- minimally invasive arthroscopy;
- UZD examination;
- Ct;
- MRI;
- Scintigraphy (as indicated).
The aim of the diagnosis of radiation is to determine joint changes and assess the condition of the cartilage.
Treatment
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint is a long process.The duration of treatment is due to the fact that the cartilage tissue is repaired very slowly and in some cases it is completely impossible to restore the joint.
Modern methods of treating arthrosis in the knee joint include comprehensive measures aimed at eliminating inflammation, normalizing lifestyle and improving metabolism of cartilage tissue.
There are such methods for therapy:
- medication;
- Exercise and massage;
- folk medicine;
- surgical interventions.
The doctor prescribes treatment based on the duration of the disease, the stage of development and the clinical manifestations of the disease.
Drugs
The purpose of the medication is to relieve pain and inflammatory reaction.For this purpose, the following drugs are prescribed:
- non -steroid anti -inflammation;
- chondroprotectors;
- glucocorticoid;
- cytostatic.
Tablets from the arthrosis of the knee joint have many side effects, and treatment requires observation of the condition of the stomach and the kidneys.
Often joint drugs are prescribed for a long time, so the least toxic drugs should be selected.
Exercise
Treatment of arthrosis with exercise is intended to strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the knee.With dosage loads in the patient's joint cartilage, the metabolism improves and regeneration processes accelerate.
Exercises should be selected separately, taking into account the stage of the patient's illness and physical abilities.
Massage
Massage of the knee joint allows you to improve your blood flow and relieve discomfort.Proper massage can prevent the appearance of ankilosis and fake joints.
Folk
Treatment of home arthrosis of the knee joint should not be the main method of fighting pathology or can only serve as a supplement to the drug.

House management includes:
- decrease in body weight;
- Normalization of labor hygiene and compliance with the Sun system;
- Fighting inflammation.
The anti -inflammatory effect is owned by such herbs:
- Tincture of thyme and St. John's beer;
- Burdock leaves;
- white cabbage leaves;
- Infusions and decoctions from dandelion and chamomile.
Operation
The operation is prescribed with the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy or at the patient's request.One of the main indications of surgical intervention is Stage 4 of the disease according to radiological characteristics.
During surgery, surgeons can fully replace the joint with endoprothesis or change one part of it.

























